qiagen REPLI-g Mini Kit Print 國內現貨
qiagen REPLI-g Mini Kit Print 國內現貨
qiagen REPLI-g Mini Kit Print 國內現貨

For highly uniform whole genome amplification from small or precious samples
- Easy amplification with consistent yields of up to 10 µg
- Unbiased amplification of genomic loci
- Reliable results due to Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA)
- Amplified DNA highly suitable for most downstream applications
- No risk of DNA degradation during long-term storage
The REPLI-g Mini Kit provides optimized reagents for whole genome amplification (WGA) from small samples using innovative Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA) technology. The typical DNA yield of a 50 μl reaction is up to 10 μg, with an average product length greater than 10 kb (ranging between 2 kb and 100 kb). Unique REPLI-g technology delivers highly uniform WGA from a variety of small or precious sample types, including purified genomic DNA, or directly from fresh or dried blood, buccal swabs, fresh or frozen tissue, and cells. This simple and reliable method is capable of accurate and unbiased amplification of genomes and generates DNA that can be applied without further purification or quantification for downstream applications that do not require labeling. In contrast to PCR-based WGA technologies, high fidelity rates are increased up to 1000-fold, avoiding costly false positive or negative results.
The REPLI-g Mini Kit is intended for molecular biology applications. This product is not intended for the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of a disease.
See trademarks.
Unbiased amplification with Phi29 polymerase.
[A] Upon encountering secondary DNA structures, Taq polymerase may pause synthesis, slip, or dissociate from the template. This can result in inaccurate DNA amplification, incomplete loci coverage, and short fragment sizes. [B] REPLI-g Kits utilize Phi29 polymerase, which displaces secondary structures enabling accurate and highly uniform amplification of the entire genome.
Performance
High yields from a variety of samples, suitable for numerous applications
With the REPLI-g Mini Kit, various clinical and non-clinical research samples can be used, including genomic DNA, fresh or dried blood, fresh or frozen tissue, and cells. Typical DNA yields per 50 µl reaction consistently reach 10 µg (see figure "Consistent DNA yields using any sample type"), while a uniform yield of amplified DNA is usually achieved regardless of the quantity of template DNA (see figure "Uniform DNA yield from various amounts of template"). Obtaining uniform DNA yields from varying template concentrations is always important, but particularly essential for high-throughput applications, which require subsequent genetic analyses to be possible without additional measurement or adjustment of DNA concentration.
The average product length of REPLI-g amplified DNA is typically more than 10 kb, with a range between 2 kb and 100 kb, enabling downstream applications such as complex restriction enzyme analysis and long-range PCR to be carried out. REPLI-g amplified DNA is highly suited for genotyping applications, such as SNP genotyping with TaqMan® primer/probe sets (see figure "Reliable SNP genotyping "), sequencing, and STR/microsatellite analysis (see figure "Accurate genotyping").
Successfully used in next-generation sequencing
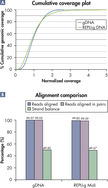
Numerous publications have demonstrated the successful utilization of REPLI-g amplified DNA for next-generation sequencing (NGS) applications that range from exome and whole genome sequencing of tumor cells, to metagenomics research, to single cell analysis (for a range of recent publications that successfully used REPLI-g in NGS, please see our WGA resource page). Since the use of whole genome amplified DNA for NGS and array applications has been debated, we detected potential factors that could influence the success of using amplified DNA for these downstream applications. We determined that the quality of input material strongly influences the success of downstream NGS experiments. If working with low quality DNA (e.g., degraded DNA) or aged tissue material, the resulting amplified DNA may not give reliable results (data not shown). However, WGA, using REPLI-g technology, on intact cells or non-degraded purified DNA shows that NGS results are comparable to those obtained with purified gDNA. Sequence coverage and alignment comparison of the genomic loci sequence indicates minimized levels of junk DNA after WGA, whereas error rates are in a similar percentage range for both amplified and genomic DNA(see figure “Comparable NGS (next-generation sequencing) results obtained using purified gDNA or REPLI-g amplified DNA”).
High fidelity whole genome amplification
REPLI-g technology provides highly uniform DNA amplification across the entire genome. Phi29 polymerase can replicate up to 70 kb without dissociating from the genomic DNA template (see figure "Schematic representation of REPLI-g amplification"). In contrast to PCR-based whole genome amplification (WGA) technologies, Phi29 polymerase has 3'→5' exonuclease proofreading activity and maintains up to 1000-fold higher fidelity compared to Taq DNA polymerase during replication. Exonuclease-resistant primers provided in the kit ensure high yields of DNA product, and the WGA buffer system is optimized for very long read length and unbiased locus representation.
REPLI-g outperforms PCR-based WGA methods
Traditional methods of genomic DNA amplification include the time-consuming process of creating EBV-transformed cell lines followed by whole genome amplification using random or degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR. Also, PCR-based methods (e.g., DOP-PCR and PEP), as generally used by other suppliers, can produce nonspecific amplification artifacts and give incomplete coverage of loci. In several cases, DNA less than 1 kb long may be generated that cannot be used in many downstream applications. In general, the resulting DNA is generated with a much higher mutation rate due to the use of the low-fidelity enzyme Taq DNA polymerase, which can lead to error-prone amplification that results in, for example, single base-pair mutations, STR contractions, and expansions. In contrast to these disadvantages, REPLI-g provides highly uniform amplification across the entire genome, with minimal locus bias and minimized mutation rates during amplification (see figures "Highly representative amplification using REPLI-g technology" and "Consistent and accurate whole genome amplification").
Principle
Unique REPLI-g technology uses the innovative, high-fidelity enzyme Phi 29 polymerase to amplify complex genomic DNA using Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA) combined with a gentle alkaline denaturation step to amplify genomic loci uniformly. The typical yield of the REPLI-g Mini Kit is up to 10 µg, and can be easily scaled down according to your needs with the REPLI-g Midi Kit, since both kits are based on the same protocol and use the same reaction volumes. The easy reaction set-up and very low handling time of approximately 15 minutes makes REPLI-g an easy and reliable method to use when complete and unbiased locus representation is needed from limited or precious samples.
Amplification principle
REPLI-g uses isothermal genome amplification, termed Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA), which involves the binding of random hexamers to denatured DNA followed by strand displacement synthesis at a constant temperature with the enzyme Phi29 polymerase. Additional priming events occur on each displaced strand that serve as a template, enabling generation of high yields of amplified DNA (see figure “Schematic representation of REPLI-g amplification”). Phi 29 polymerase, a phage derived enzyme, is a DNA polymerase with 3'→5' prime exonuclease activity (proofreading activity) that delivers up to 1000-fold higher fidelity compared to Taq DNA polymerase. Supported by the unique, optimized REPLI-g buffer system, Phi 29 polymerase easily solves secondary structures such as hairpin loops, thereby preventing slipping, stoppage, and dissociation of the polymerase during amplification. This enables the generation of DNA fragments up to 100 kb without sequence bias (see figure "Unbiased amplification with Phi 29 polymerase").
Alkaline denaturation of DNA
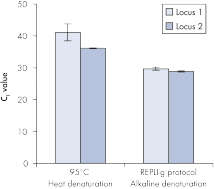
Genomic DNA must be denatured before use in enzymatic amplification procedures, which is often accomplished using harsh methods such as incubation at elevated temperatures (heat incubation) or increased pH (chemical alkaline incubation). The REPLI-g Midi Kit uses gentle alkaline incubation, allowing uniform DNA denaturation with very low DNA fragmentation or generation of abasic sites. This results in amplified DNA with very high integrity, and maximizes the length of amplified fragments so that genomic loci and sequences are uniformly represented. With the REPLI-g Mini Kit, reliable results without false positive or negative data are ensured in subsequent downstream applications, unlike with other WGA technologies that use heat-induced denaturation that can damage template DNA, leading to biased and underrepresented loci (see figure "Effect of heat and alkaline denaturation on loci representation").
Procedure
Simple, one tube procedure
The REPLI-g Mini Kit uses a simple and reliable method to achieve accurate genome amplification from small quantities of isolated target genomic DNA, or directly from whole blood, dried blood cards, buffy coat, and tissue culture cells (see figure "REPLI-g Mini and Midi procedure"). The addition of lysis buffer, which both lysis the sample material and denatures the DNA, is followed by a short minute incubation (see figure "REPLI-g Mini and Midi procedure"). After neutralization, master mix (including REPLI-g Mini DNA Polymerase) is added and the isothermal amplification reaction proceeds overnight at 30°C. REPLI-g amplified DNA can be stored long-term at –20°C with no negative effects (see figure "Consistent long-term stability").
Select the REPLI-g Kit most suited to your specific requirements from our complete range of dedicated REPLI-g products (see table).
| REPLI-g Single Cell | REPLI-g Mini | REPLI-g UltraFast Mini | REPLI-g Midi | REPLI-g Screening | REPLI-g FFPE | REPLI-g Mitochondrial DNA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Starting material | Single cells, gDNA | Purifed gDNA, blood, cells | Purifed gDNA, blood, cells | FFPE tissue, purified gDNA from FFPE tissue | Purified gDNA | ||
| (Protocols for other starting materials available from ) | |||||||
| Input amount | Single cells, 2–1000 cells, tissue, purified gDNA (1–10 ng) | >10 ng gDNA, 0.5 µl blood or cells (>600 cells/µl) | >10 ng gDNA, 0.5 µl blood or cells (>600 cells/µl) | Section (1 cm diamter, 10–40 µm thick); >100 ng gDNA | >1 ng purified gDNA | ||
| Yield (µg/reaction) | 40 | 10 | 7–10 | 40 | 8 | Standard yield: ≤10; High yield: ≤40 | 3–5 |
| Reaction time | 8–16 h | 10–16 h | 1.5 h | 8–16 h | 12–16 h | Standard yield: 4 h; High yield: 10 h | 8 h |
| Hands-on time | 15 min | 15 min | 15 min | 15 min | 15 min | 40 min | 15 min |
| Format | Tube | Tube | Tube | Tube | Plate | Tube | Tube |
Applications
REPLI-g amplified genomic can be used in a variety of downstream applications, including:
- SNP genotyping with TaqMan® primer/probe sets
- qPCR- and PCR-based mutation detection
- Next-generation sequencing
- STR/microsatellite analysis
- Sanger sequencing
- RFLP and Southern blot analysis
- Array technologies, such as comparative genomic hybridization
Features | Specifications |
| Amplification | Whole genomic DNA |
| Applications | Genotyping, hybridization, RFLP |
| Denaturation step | Alkaline |
| Maximum input volume | >10 ng DNA, 0.1– 0.5 µl whole blood, >600 cells/µl |
| Minimal pipetting volume needed | 0.5 µl |
| Quality assessment | No |
| Reaction time | 8–16 hours (overnight) |
| Reaction volume | 50 µl |
| Samples per run (throughput) | Mid |
| Starting amount of DNA | >10 ng purified genomic DNA |
| Starting material | Genomic DNA, blood, cells, tissue |
| Technology | Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA) |
| Yield | 10–40 µg |


 7
7